
Main activity targets
Level(s):
Digital Competency Framework Components (QC):
Subject(s):
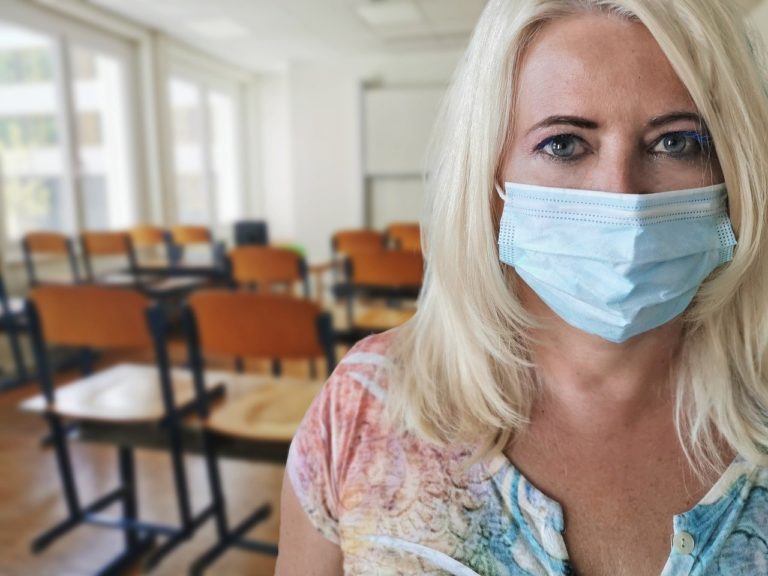
Last December, in the city of Wuhan, China, a virus usually linked to animals was transmitted to a human for the first time. The coronavirus COVID-19 comes from the same family of viruses that usually affects the respiratory tract. It is in the same family as the common cold, the flu, and other more serious respiratory illnesses. When humans are infected with COVID-19, they experience symptoms such as fever, coughing, and difficulty breathing similar to pneumonia.
The coronavirus COVID-19 was transmitted from a living animal to a human during a visit to one of Wuhan’s markets. There is a hypothesis that suggests the virus comes from a snake, a bat, or a pangolin because proteins from this virus are more likely to act in the body of those animals. However, this hypothesis remains to be validated and has not been proven yet. We are still investigating the origin of the virus by checking the animals sold at that market.
The number of people infected with the virus increases exponentially and, unfortunately, some vulnerable people die (around 4%). What is worrisome is that there is no treatment or vaccine to stop the progression of this virus. Scientists are studying the virus to know more about it and eventually find solutions and avoid its contagion. This Web application shows, in real time, the number of people infected across the world.
To ensure that the virus does not spread around the globe, very strict measures have been put in place. City borders have been closed in affected regions, preventing people from going in or out of those areas. Public transit is also stopped. At airport customs, travellers are thoroughly questioned about their health. Those who have visited affected regions are under surveillance and isolated until the end of the period when symptoms would usually appear. In hospitals, intense cleaning and disinfecting measures have been put in place. In Wuhan, a hospital of 1000 beds has been built in a record time (10 days) to treat infected people.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) tracts the number of confirmed cases in each country and follows closely the progression of the virus. It provides guidance on sanitary precautions to implement in each country, and works towards finding solutions not only to cure patients, but also to stop the propagation.
What does “flattening the curve” mean in COVID-19 case? Find a definition of this expression by looking for credible sources of information on the web.
At the end of this unit, students will be able to evaluate the seriousness of the epidemic and understand the security measures that need to be taken to avoid infection without causing public panics.
Toolbox
PDF: What I Know > What I Want to Know > What I Learnt
Obtenez une suggestion de guide d'activités à découvrir chaque vendredi!
Pour vous offrir une expérience optimale, nous utilisons certaines technologies — dont les témoins (cookies) — afin de stocker et/ou d’accéder à des informations liées à votre utilisation du site. Votre consentement nous aide à mieux comprendre votre parcours de navigation et à améliorer nos contenus et services. Le refus ou le retrait de votre consentement pourrait toutefois limiter le fonctionnement de certaines fonctionnalités.